Comprehensive health insurance coverage also as major medical health insurance. new individual/family small-group major medical policies sold January 1, 2014, cover ten essential health benefits outlined the Affordable Care Act ( ACA ) no annual lifetime benefit caps.
 A high-deductible health plan, HDHP, be one the types health insurance — HMO, PPO, EPO POS — follows rules order be "HSA-eligible." HDHPs .
A high-deductible health plan, HDHP, be one the types health insurance — HMO, PPO, EPO POS — follows rules order be "HSA-eligible." HDHPs .
 Find individual family health insurance plans your area. Get quotes, get finding plan, learn about health insurance options.
Find individual family health insurance plans your area. Get quotes, get finding plan, learn about health insurance options.
 Major medical insurance comprehensive health insurance covers medical services, hospitalizations, doctor visits, prescriptions, mental health other types healthcare. vast .
Major medical insurance comprehensive health insurance covers medical services, hospitalizations, doctor visits, prescriptions, mental health other types healthcare. vast .
 A type health insurance plan usually limits coverage care doctors work or contract the HMO. generally won't cover out-of-network care in emergency. HMO require to live work its service area be eligible coverage. HMOs provide integrated care focus prevention wellness.
A type health insurance plan usually limits coverage care doctors work or contract the HMO. generally won't cover out-of-network care in emergency. HMO require to live work its service area be eligible coverage. HMOs provide integrated care focus prevention wellness.
 The amount pay your health insurance depend where live, income, the size your household. Health insurance costs include premium, is you pay your insurance plan month. But, you seek health care services, may have pay out-of-pocket costs.
The amount pay your health insurance depend where live, income, the size your household. Health insurance costs include premium, is you pay your insurance plan month. But, you seek health care services, may have pay out-of-pocket costs.
 In addition, CHIP (Children's Health Insurance Program) enrollment also year-round, eligibility extends higher income levels Medicaid. good news that your application successful, Medicaid coverage be effective on date the application the day the month you apply.And e ven news some applicants: .
In addition, CHIP (Children's Health Insurance Program) enrollment also year-round, eligibility extends higher income levels Medicaid. good news that your application successful, Medicaid coverage be effective on date the application the day the month you apply.And e ven news some applicants: .
 Members praised Aetna's comprehensive network coverage efficient claims processing. However, members criticized company's customer service, claim denials, out-of-pocket costs .
Members praised Aetna's comprehensive network coverage efficient claims processing. However, members criticized company's customer service, claim denials, out-of-pocket costs .
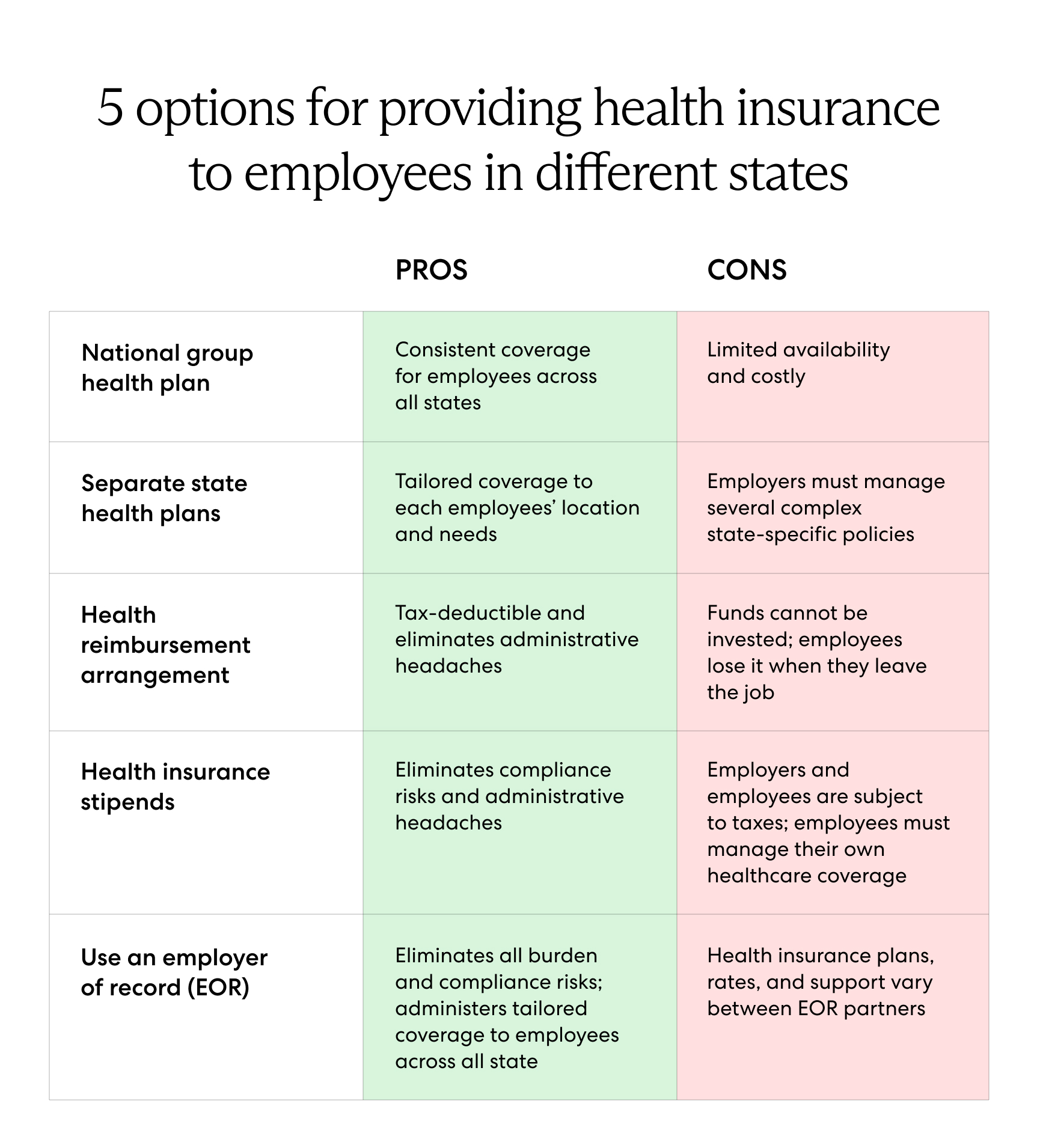 Right now, Americans ever buying comprehensive Affordable Care Act (ACA)-compliant individual family health insurance plans. 2 ACA created income-based subsidies make plans affordable. 3 those subsidies now larger more widely as result the American Rescue Plan Inflation Reduction Act, many enrollees eligible zero .
Right now, Americans ever buying comprehensive Affordable Care Act (ACA)-compliant individual family health insurance plans. 2 ACA created income-based subsidies make plans affordable. 3 those subsidies now larger more widely as result the American Rescue Plan Inflation Reduction Act, many enrollees eligible zero .
 Other ways get health insurance. Individual health insurance an option, there other ways an employer plan a person get coverage: Short-term plans. plans don't offer same benefits a normal health insurance plan. Insurers aren't required provide comprehensive benefits.
Other ways get health insurance. Individual health insurance an option, there other ways an employer plan a person get coverage: Short-term plans. plans don't offer same benefits a normal health insurance plan. Insurers aren't required provide comprehensive benefits.
 How well do you know your health insurance coverage? | Morris Hospital
How well do you know your health insurance coverage? | Morris Hospital
 How to Get Health Insurance - Ramsey
How to Get Health Insurance - Ramsey
 How to Choose a Comprehensive Health Insurance That Is Affordable
How to Choose a Comprehensive Health Insurance That Is Affordable
 How to Get Health Insurance: Your Step-by-Step Guide to Securing Vital
How to Get Health Insurance: Your Step-by-Step Guide to Securing Vital
 A guide on how to get a health insurance
A guide on how to get a health insurance
 How To Get Health Insurance Online Instruction Infographics Stock
How To Get Health Insurance Online Instruction Infographics Stock
 Know About Health Insurance Benefits for Medical Emergencies
Know About Health Insurance Benefits for Medical Emergencies
![What Is Comprehensive Health Insurance [6 Benefits Of It] What Is Comprehensive Health Insurance [6 Benefits Of It]](https://global-uploads.webflow.com/61b1902b9f28a2a852f7012f/61d8002345ab265e68aa4a12_What-Is-Comprehensive-Health-Insurance-OG.png) What Is Comprehensive Health Insurance [6 Benefits Of It]
What Is Comprehensive Health Insurance [6 Benefits Of It]
![[Infographic] Health Insurance 101 | Keystone Financial Group [Infographic] Health Insurance 101 | Keystone Financial Group](https://fionaleung2.advisorwebsite.com/sites/default/files/users/fionaleung2/images/healthinsurance101.png) [Infographic] Health Insurance 101 | Keystone Financial Group
[Infographic] Health Insurance 101 | Keystone Financial Group
 Comprehensive Health Insurance Plans - Coverage & Benefits
Comprehensive Health Insurance Plans - Coverage & Benefits
 How to get health insurance in 2021 special enrollment period - YouTube
How to get health insurance in 2021 special enrollment period - YouTube

